VAXNEUVANCE in infants, children and adolescents
VAXNEUVANCE®▼ (pneumococcal polysaccharide conjugate vaccine (15-valent, adsorbed)) can help protect your infant, child and adolescent patients against 15 pneumococcal serotypes1,2
Prescribing Information (Great Britain) & Prescribing Information (Northern Ireland) [External links]
VAXNEUVANCE is indicated for active immunisation for the prevention of invasive disease, pneumonia and acute otitis media caused by Streptococcus pneumoniae in infants, children and adolescents from 6 weeks to less than 18 years of age. 1,2
VAXNEUVANCE is indicated for active immunisation for the prevention of invasive disease and pneumonia caused by Streptococcus pneumoniae in individuals 18 years of age and older.1,2
Please refer to the VAXNEUVANCE SmPC for further information before making any prescribing decisions. The use of VAXNEUVANCE should be in accordance with official recommendations.1,2

VAXNEUVANCE contains two additional Streptococcus pneumoniae serotypes versus PCV13
(13-valent pneumococcal conjugate vaccine)1-3
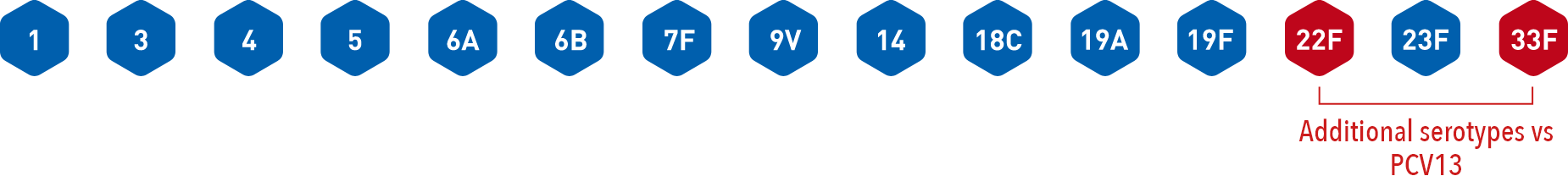
PCV13 contains 13 Streptococcus pneumoniae serotypes3


Study design4
Background
This Phase 3 study evaluated the safety and immunogenicity of VAXNEUVANCE compared with PCV13 administered as a 2+1 dosing regimen in healthy and pre-term infants. This was administered concomitantly with other paediatric vaccines including diphtheria, tetanus and pertussis (DTaP)/inactivated poliovirus (IPV)/Haemophilus influenzae type B (Hib)/hepatitis B (HepB) and rotavirus vaccines.
Methods
- PNEU-PED-EU-1 was a Phase 3, multicentre, randomised, double-blind, active comparator-controlled study to evaluate the safety, tolerability and immunogenicity of a three-dose regimen of VAXNEUVANCE in healthy infants
- Healthy infants were randomised in a 1:1 ratio to receive either VAXNEUVANCE or PCV13 administered as a two-dose primary series at 2 and 4 months of age, followed by a toddler dose at 11–15 months of age
- Healthy preterm (<37 weeks) infants received a 3 + 1 dose schedule (three-dose primary series followed by a toddler dose) of PCV at approximately 2, 3, 4, and 11–15 months of age
Primary objectives
Safety and tolerability: To evaluate the safety and tolerability of VAXNEUVANCE with respect to the proportion of participants with adverse events (AEs).
Immunogenicity: To compare the anti-pneumococcal polysaccharide (PnPs) serotype-specific IgG response rates (proportion of participants meeting serotype-specific IgG threshold value of ≥0.35 μg/ml), as well as immunoglobulin G (IgG) geometric mean concentrations (GMCs) at 30 days post-toddler dose (PTD) (post-dose 3 for full-term infants; post-dose 4 for pre-term infants) for participants administered VAXNEUVANCE versus PCV13.
Secondary objectives
- To compare the antigen-specific response rates to each antigen included in the DTaP/IPV/Hib/HepB vaccine 30 days PTD for participants administered VAXNEUVANCE versus PCV13
- To compare anti-rotavirus immunoglobulin A (IgA) geometric mean titres (GMTs) at 30 days post-primary series (PPS) for participants administered the rotavirus vaccine concomitantly with VAXNEUVANCE versus PCV13
- To evaluate the anti-PnPs serotype-specific opsonophagocytic activity (OPA) GMTs and response rates at 30 days PTD by each vaccination group
Results
- Of 1188 eligible participants who were randomised, 1184 were included in the final analysis:
- In the VAXNEUVANCE group (N=591), 588 participants were vaccinated with at least one dose of VAXNEUVANCE
- In the PCV13 group (N=593), 591 participants were vaccinated with at least one dose of PCV13
- Reasons for discontinuation included protocol deviation, withdrawal, physician decision and loss to follow-up
- Across the VAXNEUVANCE and PCV13 groups, demographic and baseline characteristics were generally comparable
- Approximately 6% of participants were pre-term infants
Safety
- The proportions of participants with AEs, including injection-site, systemic and vaccine-related AEs, and serious adverse events (SAEs) were generally comparable between vaccination groups
- No deaths were reported in either group
- The proportions of participants with solicited injection-site AEs and systemic AEs were generally comparable across both vaccination groups
- Higher proportions of participants in the VAXNEUVANCE group compared with the PCV13 group were observed with solicited AEs of injection-site pain and irritability
- Of the participants in the VAXNEUVANCE group with solicited AEs, the majority had events with a maximum intensity of mild or moderate and were of short duration (≤3 days)
- The most frequently reported AEs following vaccination with VAXNEUVANCE were irritability, somnolence and injection-site erythema
- No vaccine-related SAEs were reported in participants receiving VAXNEUVANCE
- The majority of participants in the VAXNEUVANCE group reported body temperature measurements <38.5°C and, overall, temperature distribution was comparable to PCV13 and consistent with the overall study population
- The numbers of participants with a maximum temperature ≥39°C were 18.9% and 14.6% in the VAXNEUVANCE and PCV13 groups, respectively; however, the majority of these were below 40.5°C
- VAXNEUVANCE was well tolerated in pre-term participants, with a safety profile comparable to PCV13 and consistent with the overall study population (including full-term and pre-term infants)
Immunogenicity results
- VAXNEUVANCE met non-inferiority criteria for the 13 shared serotypes, as assessed by the proportions of participants meeting the threshold value of ≥0.35 μg/ml (response rate) for each serotype and serotype-specific IgG GMCs at 30 days PTD
- VAXNEUVANCE met superiority criteria for the two additional serotypes (22F and 33F), as assessed by response rates and serotype-specific IgG GMCs at 30 days PTD
Conclusions
In healthy infants ~2 months of age:
- VAXNEUVANCE is well tolerated, with a safety profile generally comparable to PCV13
- VAXNEUVANCE is non-inferior to PCV13 for the 13 shared serotypes and superior to PCV13 for the two additional serotypes (22F and 33F) at 30 days PTD, as assessed by serotype-specific IgG responses (response rates and GMCs)
- VAXNEUVANCE induces functional antibodies (OPA) capable of bactericidal killing of Streptococcus pneumoniae PPS and PTD
- VAXNEUVANCE can be administered concomitantly with licensed paediatric vaccines (DTaP/IPV/Hib/HepB and rotavirus)
The pivotal PNEU-PED-EU-1 phase 3 study in healthy infants compared the safety and immunogenicity of VAXNEUVANCE and PCV13. In this study, VAXNEUVANCE demonstrated:
- non-inferior immune responses to 13 shared serotypes
- superiority criteria for serotypes 22F and 33F
These results support the routine use of VAXNEUVANCE in infants.
References
- VAXNEUVANCE Summary of Product Characteristics for GB.
- VAXNEUVANCE Summary of Product Characteristics for NI.
- PREVENAR 13® Pneumococcal polysaccharide conjugate vaccine (13-valent, adsorbed) Summary of Product Characteristics.
- Martinon-Torres F, et al. A Phase III, multicenter, randomized, double-blind, active comparator-controlled study to evaluate the safety, tolerability, and immunogenicity of V114 compared with PCV13 in healthy infants (PNEU-PED-EU-1) Vaccine. 2023; 41(21):3387-3398.
- Wilck M, et al. A phase 3 randomized, double-blind, comparator-controlled study to evaluate safety, tolerability and immunogenicity of V114 pneumococcal vaccine in hematopoietic cell transplant recipients (PNEU-STEM). Hemasphere. 2022 Jun 23;(6 Suppl):1457-1458.
- Banniettis N, et al. A phase III, multicenter, randomized, double-blind, active comparator-controlled study to evaluate the safety, tolerability, and immunogenicity of catch-up vaccination regimens of V114, a 15-valent pneumococcal conjugate vaccine, in healthy infants, children, and adolescents (PNEU-PLAN). Vaccine. 2022 Oct 19;40(44):6315-6325.
- Quinn CT, et al. Safety and immunogenicity of V114, a 15-valent pneumococcal conjugate vaccine, in children with SCD: a V114-023 (PNEU-SICKLE) study. Blood Adv. 2023 Feb 14;7(3):414-421.
- Benfield T, et al. Safety, tolerability, and immunogenicity of V114 pneumococcal vaccine compared with PCV13 in a 2+1 regimen in healthy infants: A phase III study (PNEU-PED-EU-2). Vaccine. 2023. 41(15):2456-2465.
Supporting documentation
Prescribing Information (Great Britain) & Prescribing Information (Northern Ireland)
By clicking the links above you will leave the MSD Connect website and be taken to the emc PI portal website.
