Safety Information
Doravirine safety information: adverse events
DELSTRIGO® (Doravirine/Lamivudine/tenofovir disoproxil fumarate)
Prescribing Information (United Kingdom) [External link]
PIFELTRO® (doravirine)
Prescribing Information (United Kingdom) [External link]
Doravirine/3TC/TDF = DELSTRIGO (doravirine/lamivudine/tenofovir disoproxil fumarate).
PIFELTRO® (doravirine) 100 mg film-coated tablet is indicated, in combination with other antiretroviral medicinal products, for the treatment of adults, and adolescents aged 12 years and older, weighing at least 35 kg, infected with HIV-1, without past or present evidence of resistance to the NNRTI class.
DELSTRIGO® (100 mg doravirine/300 mg lamivudine/300 mg tenofovir disoproxil fumarate, equivalent to 245 mg tenofovir disoproxil) is indicated for the treatment of adults infected with HIV-1 without past or present evidence of resistance to the NNRTI class, lamivudine or tenofovir.
DELSTRIGO® is also indicated for the treatment of adolescents aged 12 years and older weighing at least 35 kg, who are infected with HIV-1, without past or present evidence of resistance to the NNRTI class, lamivudine, or tenofovir and who have experienced toxicities which preclude the use of other regimens that do not contain tenofovir disoproxil.
Please refer to the relevant Summary of Product Characteristics for full details of adverse events and contraindications before prescribing.
144-week results of DRIVE-SHIFT1
Most common adverse events of any causality through to Week 1441

| Nasopharyngitis | 16.2% |
| Headache | 12.3% |
| Diarrhoea | 9.1% |
Adapted from Kumar P et al. 20211
These events were rated as mild intensity by 73.6% (nasopharyngitis), 74.1% (headache) and 75% (diarrhoea) of participants.1
Overall 4.1% participants discontinued due to adverse events through to Week 144.1
96-week results of DRIVE-AHEAD2 and DRIVE-FORWARD3
Summary of all cause adverse events with ≥10% incidence in either treatment group through Week 96 in DRIVE-AHEAD2
| AEs | DOR/3TC/TDF (n=364) | EFV/FTC/TDF (n=364) |
|---|---|---|
| Neuropsychiatric AE (prespecified)a | 26% | 59% |
| Adverse eventb | ||
| Headache | 16% | 15% |
| Nasopharyngitis | 14% | 12% |
| Diarrhoea | 13% | 16% |
| Upper respiratory tract infection | 11% | 8% |
| Dizziness | 10% | 38% |
| Nausea | 9% | 12% |
| Insomnia | 7% | 10% |
| Rash | 6% | 12% |
| Abnormal dreams | 5% | 12% |
aPrespecified AEs included dizziness, sleep disorders and disturbances. altered sensorium, depression and suicide/self-injury, and psychosis and psychotic disorders.
bAEs with ≥10% incidence in either treatment group.
3TC = Lamivudine; AE = Adverse Event; DOR = Doravirine; EFV = Efavirenz; FTC = Emtricitabine; TDF = Tenofovir Disoproxil Fumarate.
Proportion of participants with neuropsychiatric adverse events in prespecified categories through Week 96 in DRIVE-AHEAD2
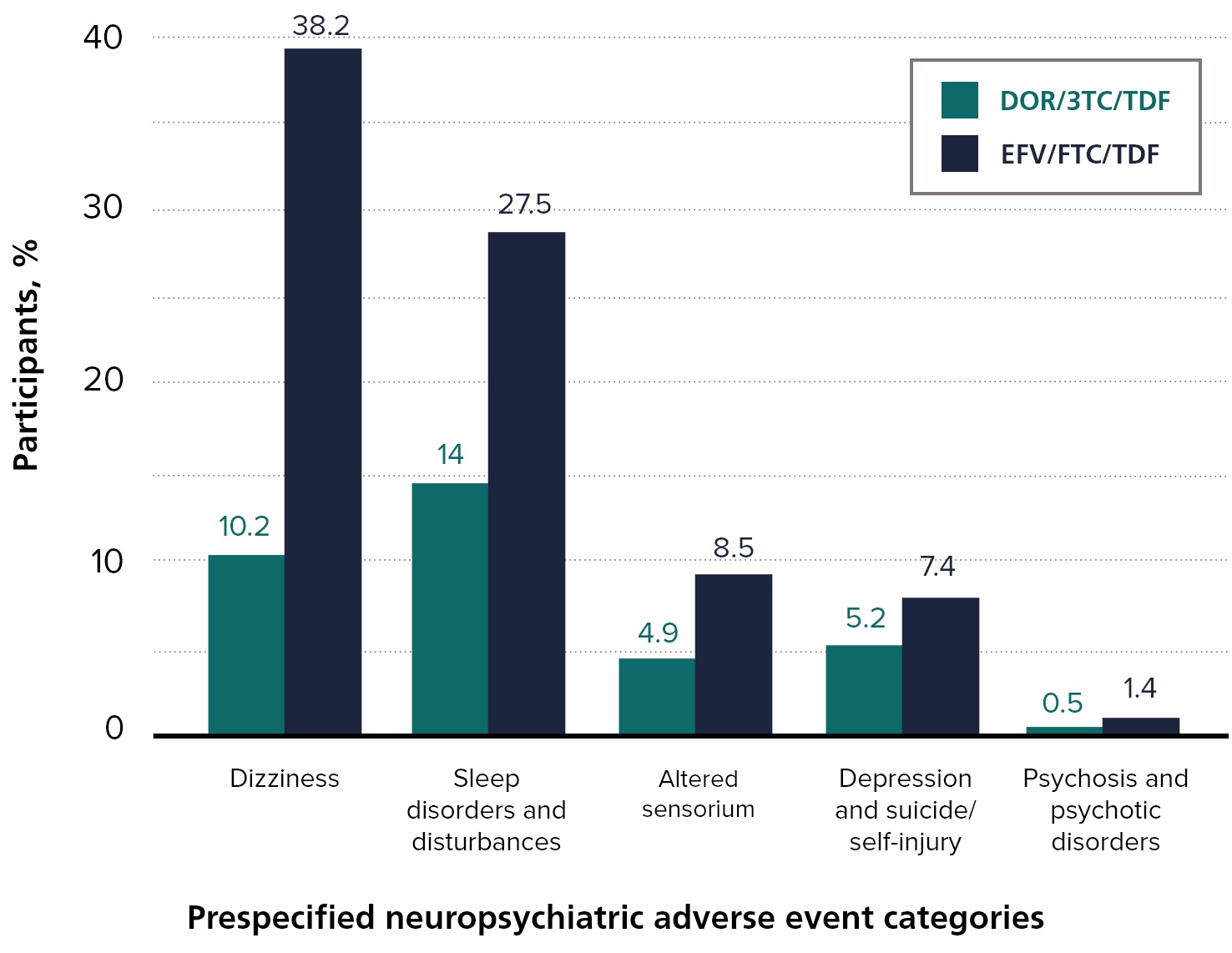

Consistent with results from Weeks 0–48,4 overall neuropsychiatric AEs (Weeks 0–96) were less common for DOR/3TC/TDF (26.4%) than for EFV/FTC/ TDF (58.5%).2
The majority of reported neuropsychiatric AEs occurred before Week 48 for both groups, with minimal difference in new-onset neuropsychiatric AEs between groups after Week 48.2
3TC = Lamivudine; DOR = Doravirine; EFV = Efavirenz; FTC = Emtricitabine; TDF = Tenofovir Disoproxil Fumarate.
Summary of all-cause adverse events with ≥5% incidence in either treatment group through Week 96 in DRIVE-FORWARD3
| PIFELTRO + 2 NRTIs once daily (n=383) | DRV/r + 2 NRTIs once daily (n=383) | |
|---|---|---|
| Adverse eventa | ||
| Abdominal pain upper | 5% | 3% |
| Back pain | 7% | 3% |
| Bronchitis | 6% | 8% |
| Cough | 6% | 3% |
| Diarrhoea | 17% | 24% |
| Dizziness | 5% | 5% |
| Fatigue | 9% | 6% |
| Headache | 15% | 12% |
| Insomnia | 5% | 5% |
| Nausea | 12% | 14% |
| Syphilis | 6% | 6% |
| Upper respiratory tract infection | 13% | 8% |
| Viral upper respiratory tract infection | 11% | 13% |
aAEs with ≥5% incidence in either treatment group.
NRTI = Nucleoside Reverse Transcriptase Inhibitor; DRV/r = Darunavir/Ritonavir.
Neuropsychiatric adverse events through Week 48 in DRIVE-FORWARD5
This was an interim analysis only completed in the initial study and reported in the Week 48 publication
Neuropsychiatric events in the DRIVE-FORWARD study include disturbances in attention, dizziness, somnolence, abnormal dreams, confusion, depressed mood, depression, insomnia, major depression, nightmares, and psychotic disorder. No participants discontinued study treatment due to neuropsychiatric adverse events.
There is not sufficient clinical evidence to support the use of doravirine in patients infected with HIV-1 with evidence of resistance to the NNRTI class. All patients with HIV-1 should be tested for the presence of hepatitis B virus (HBV) before initiating antiretroviral therapy. Caution should be given to prescribing doravirine with medicinal products that may reduce the exposure of doravirine through induction of CYP3A enzymes.
Delstrigo and Pifeltro contains lactose monohydrate. Patients with rare hereditary problems of galactose intolerance, total lactase deficiency or glucose-galactose malabsorption should not take this medicine.
Delstrigo
Renal impairment, including cases of acute renal failure and Fanconi syndrome (renal tubular injury with severe hypophosphataemia), has been reported with the use of tenofovir disoproxil, a component of Delstrigo. It is recommended that estimated CrCl be assessed in all patients prior to initiating therapy and as clinically appropriate during therapy with Delstrigo. Delstrigo should be discontinued if estimated CrCl declines below 50 mL/min. Assessment of bone mineral density should be considered for patients who have a history of pathologic bone fracture or other risk factors for osteoporosis or bone loss. Hypophosphatemia and osteomalacia secondary to proximal renal tubulopathy should be considered in patients at risk of renal dysfunction who present with persistent or worsening bone or muscle symptoms.
Pregnancy and Lactation: Use of Pifeltro and Delstrigo should be avoided during pregnancy. Breastfeeding is not recommended.
UNDESIRABLE EFFECTS
Refer to SmPC for complete information on side-effects.
Pifeltro and Delstrigo:
Common: abnormal dreams, insomnia, headache, dizziness, somnolence, cough, nasal symptoms, nausea, diarrhoea, flatulence, abdominal pain, vomiting, rash, fatigue, increased alanine aminotransferase increased.
Uncommon: Hypophosphataemia, nightmare, depression, anxiety, irritability, confusional state, suicidal ideation, disturbance in attention, memory impairment, paraesthesia, hypertonia, poor quality sleep, hypertension, constipation, abdominal discomfort, abdominal distension, dyspepsia, faeces soft, gastrointestinal motility disorder, pruritus, myalgia, arthralgia, asthenia, malaise, lipase increased, aspartate aminotransferase increased, amylase increased, haemoglobin decreased.
Rare: Rash pustular, hypomagnesaemia, aggression, hallucination, adjustment disorder, mood altered, somnambulism, dyspnoea, tonsillar hypertrophy, dermatitis allergic, acute kidney injury, renal disorder, calculus urinary, nephrolithiasis, chest pain, chills, pain, thirst, blood creatine phosphokinase increased.
Delstrigo:
Common: Alopecia, muscle disorders, fever.
Uncommon: Neutropenia, anaemia, thrombocytopenia, hypokalaemia pancreatitis, rhabdomyolysis, proximal renal tubulopathy (including Fanconi syndrome).
Rare: Acute renal failure, renal failure, acute tubular necrosis, musculoskeletal pain, osteomalacia, myopathy, hepatic steatosis, hepatitis.
Very rare: Peripheral neuropathy.
Delstrigo: Cases of lactic acidosis have been reported with tenofovir disoproxil alone or in combination with other antiretrovirals. Patients with predisposing factors are at increased risk of experiencing severe lactic acidosis during tenofovir disoproxil treatment, including fatal outcomes.
Hypersensitivity to the active substance or to any of the excipients listed in section 6.1 of the SmPC.
Co-administration with medicinal products that are strong cytochrome P450 CYP3A enzyme inducers is contraindicated as significant decreases in doravirine plasma concentrations are expected to occur, which may decrease the effectiveness of PIFELTRO (see sections 4.4 and 4.5 in the SmPC). These medicinal products include, but are not limited, to the following:
- Carbamazepine, oxcarbazepine, phenobarbital, phenytoin
- Rifampicin, rifapentine
- St. John’s wort (Hypericum perforatum)
- Mitotane
- Enzalutamide
- Lumacaftor
References
- Kumar P et al. Switching to Doravirine/Lamivudine/Tenofovir Disoproxil Fumarate (DOR/3TC/TDF) Maintains HIV-1 Virologic Suppression Through Week 144 in the DRIVE-SHIFT Trial. J Acquir Immune Defic Syndr. 2021 Feb 17. doi: 10.1097/QAI.0000000000002642. Epub ahead of print.
- Orkin C et al. Doravirine/Lamivudine/Tenofovir Disoproxil Fumarate (TDF) Versus Efavirenz/Emtricitabine/TDF in Treatment naive Adults With Human Immunodeficiency Virus Type 1 Infection: Week 96 Results of the Randomized, Double blind, Phase 3 DRIVE-AHEAD Noninferiority Trial. Clinical Infectious Diseases. 2020: 1-10.
- Molina JM et al. Doravirine versus ritonavir-boosted darunavir in antiretroviral-naive adults with HIV-1 (DRIVE-FORWARD):96-week results of a randomised, double-blind, non-inferiority, phase 3 trial. Lancet HIV. 2020;7: 16-26.
- Orkin C et al. Doravirine/lamivudine/tenofovir disoproxil fumarate is non-inferior to efavirenz/emtricitabine/tenofovir disoproxil fumarate in treatment-naive adults with human immunodeficiency virus-1 infection: week 48 results of the DRIVE-AHEAD trial. Clin Infect Dis. 2019;68(4):535-544.
- Molina JM et al. Doravirine versus ritonavir-boosted darunavir in antiretroviral-naive adults with HIV-1 (DRIVE-FORWARD): 48-week results of a randomised, double-blind, phase 3, non-inferiority trial. Lancet HIV. 2018;5:e211-e220.
- DELSTRIGO Summary of Product Characteristics.
- PIFELTRO Summary of Product Characteristics.
Supporting documentation
DELSTRIGO® Prescribing Information (United Kingdom) [External link]
PIFELTRO® Prescribing Information (United Kingdom) [External link]
By clicking the links above you will leave the MSD Connect website and be taken to the emc website
